Palm oil vs palm kernel oil: What's the difference?
The term "palm oil", as the Malaysian Palm Oil Council (MPOC) defines it, actually encompasses several types of oil derived from the palm tree, including palm oil and palm kernel oil, and their respective fractionated components.
Because of its nearly equal fatty acids composition - 50% saturated and 50% unsaturated - palm oil can be fractionated for different uses, i.e. partially crystallized and separated into a high melting fraction or stearin (e.g. formulation of margarine, shortening, confectionery and vegetable ghee); and a low melting fraction or olein (e.g. formulation of instant noodles and fried food products).
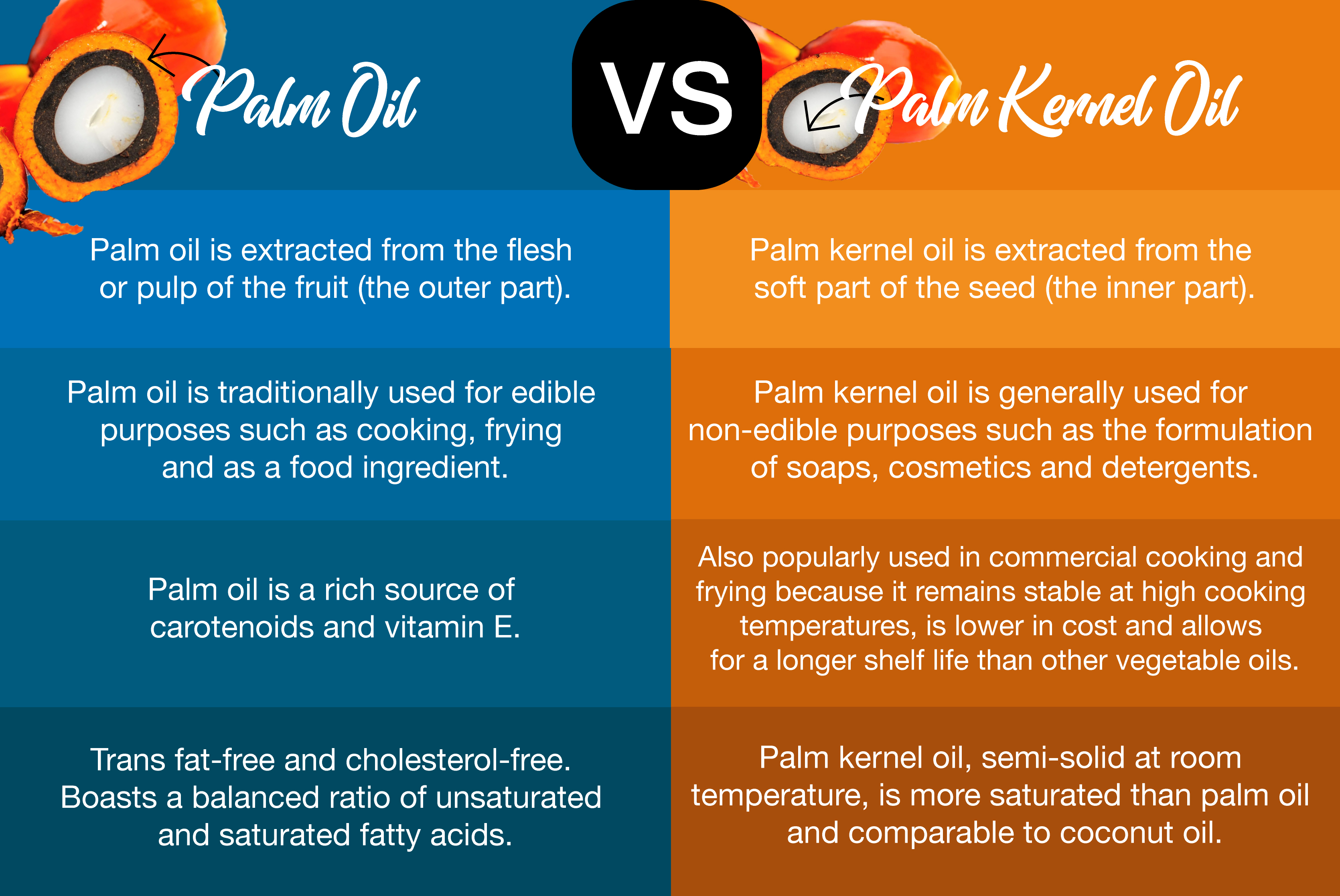
Palm oil and palm kernel oil are both versatile oils extracted from different parts of the oil palm fruit. Palm oil is extracted from the flesh or pulp of the fruit (the outer part) while palm kernel oil is extracted from the soft part of the seed (the inner part). Although both oils originate from the same fruit, palm oil is chemically and nutritionally different from palm kernel oil.
Palm oil (including its fractions) is traditionally used for edible purposes such as cooking and frying, in addition to being a choice ingredient of food formulations (e.g. shortenings and confectionery).
Palm kernel oil (including its fractions) is generally used for non-edible purposes such as the formulations of soaps, cosmetics and detergents - oleochemicals.
The versatility of both palm oil and palm kernel oil is compiled here.
Palm oil
The trans fat-free and cholesterol-free palm oil boasts a balanced ratio of unsaturated and saturated fatty acids. It generally contains 40% oleic acid (monounsaturated fatty acid), 10% linoleic acid (polyunsaturated fatty acid), 45% palmitic acid and 5% stearic acid (saturated fatty acids). This composition results in an edible oil that is suitable for use in a variety of food applications. Backed by many scientific publications, palm oil is a rich source of carotenoids and vitamin E that provides natural stability against oxidative deterioration.
Palm kernel oil
While palm oil can be fractionated into palm olein and plam stearin, palm kernel oil can also be further processed into palm kernel olein and palm kernel stearin. Palm kernel oil, semi-solid at room temperature, is more saturated than palm oil and comparable to coconut oil. It is popularly used in commercial cooking and frying because it remains stable at high cooking temperatures and is lower in cost than other oils while allowing for a longer shelf life than other vegetable oils.
What is fractionation?
Just as its name suggests, it is a process that fractionates or divides the oil into different fat components. Fractionation, which generally involves pre-heating, cooling, crystallization and filtering, is needed to separate solid phases (stearin) and liquid phases (olein) to maximize palm oil’s commercial value. The different processes are visually explained here.
RM12.50 / month
- Unlimited access to award-winning journalism
- Comment and share your opinions on all our articles
- Gift interesting stories to your friends
- Tax deductable
